自動運転 - 3次元地図生成とその応用
Autonomous Driving - Generation and Application of 3D Map
近年、高度交通システム(ITS)の分野において、自動運転の実現に向けて様々な研究開発が行われています。 その自動運転の実現には高精度な地図を整備することが非常に重要であり、自動運転のための高精度地図の研究も盛んに行われています。 特に、走行経路上のオブジェクトの三次元構造を記録した三次元地図については、自動車の自己位置推定では欠かせないものとなってきています。 このような高精度な三次元地図を整備する上で、注目されている手法の一つに、LiDARによる測位データと、車両の自己位置推定技術を組み合わせて、三次元地図を整備する手法(Mobile Mapping System; MMS)が存在します 。LiDARは建物等の幾何学的形状を正確にマッピングすることが可能である一方、これらによって測定された建物の絶対位置を決定するには、車両の自己位置推定を高精度に行わなければいけません。 しかし、周辺に建物が多数存在するような環境下においては、車両の正確な自己位置を推定することは難しいです。その結果、MMSによって測定された地図をそのまま絶対座標上で見ると、複数の観測データ間で大きな位置のずれが発生します。 MMSではこの位置のずれを補正するためには、手作業によって測量された基準点を多数用いて、キャリブレーションを行う必要があります。 そこで本研究においては、GPSをはじめとしたGNSSの測位データを用いて、壁面の絶対位置を直接推定する手法について提案しました。 周辺に建物が多数存在するような場所では、時折GNSSの搬送波が建物に反射して受信機に届きます。 このような反射波をレイトレーシング法によりシミュレーションし、観測された反射波と、シミュレーションされた反射波の差を計算することで、壁面の真の位置を推定することができます。 また、この手法を用いることで、従来手作業によって決定されていた壁面の絶対位置座標を自動的に推定し、効率化/コスト削減が可能になりました。 本手法により推定された壁面の絶対位置は、MMSの測定データを元にキャリブレーションにより正確に推定された壁面の絶対位置と比較した際に平均して1m以下の精度で一致することが実験結果により示されています。
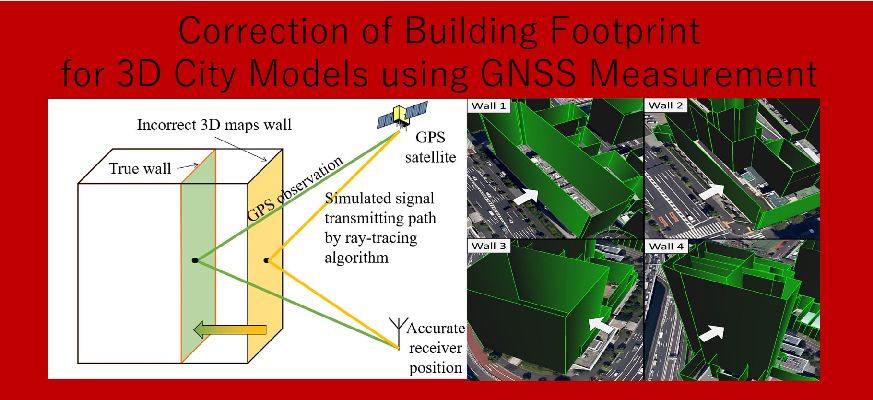
In the field of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) and autonomous driving, the estimation of the accurate ego position of vehicle or pedestrian is essential. Recently, the 3D building model becomes important aids to many positioning methods such as LiDAR and GPS positioning methods. To build the accurate 3D building model, the accurate building footprint (the boundary of the building) is required. In this study, we propose an innovative method to correct the errors of building footprint on the 3D map by using GPS NLOS measurements. In the urban canyon, a lot of GPS signals are reflected by the buildings as a NLOS satellite. These reflections are potentially capable of indicating the correct position of the buildings. By using of a rough 3D building model, we apply it with a GPS ray-tracing method to track the simulated reflection path of the NLOS GPS. Theoretically, the length of observed reflection path, which is well-known as pseudorange measurement, and the length of simulated reflection path should be very similar. However, if the 3D map is not accurate, the difference between the observed pseudorange and simulated pseudorange will be detected. To utilize this fact, the proposed method is able to estimate the true position of the wall on the 3D map. Specifically, we move the footprint of the wall which is reflected the GPS signals on the 3D map to the direction that the difference between two kinds of pseudorange will be small. When we can find the minimum value of the difference, this position of the footprint should be truth. To prove its assumption, we did the experiment in the urban canyon and we collected GPS observation data. Results show that the proposed method successfully corrected the building footprint of the wall from the rough 3D map in sub-meter accuracy.